Complex Numbers¶
The functions described in this chapter provide support for complex numbers. The algorithms take care to avoid unnecessary intermediate underflows and overflows, allowing the functions to be evaluated over as much of the complex plane as possible.
The complex types, functions and arithmetic operations are defined in
the header file cml/complex.h.
Representation of complex numbers¶
Complex numbers are represented using the type cml_complex_t. The
internal representation of this type may vary across platforms and
should not be accessed directly. The functions and macros described
below allow complex numbers to be manipulated in a portable way.
For reference, the default form of the cml_complex_t type is
given by the following struct:
typedef struct _complex
{
union
{
double p[2];
double parts[2];
struct
{
double re;
double im;
};
struct
{
double real;
double imaginary;
};
};
} cml_complex_t;
The real and imaginary part are stored in contiguous elements of a two
element array. This eliminates any padding between the real and
imaginary parts, parts[0] and parts[1], allowing the struct to
be mapped correctly onto packed complex arrays.
-
cml_complex_t
complex(double x, double y)¶ This function uses the rectangular Cartesian components
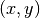 to return the complex number
to return the complex number 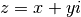 .
An inline version of this function is used when
.
An inline version of this function is used when HAVE_INLINEis defined.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_polar(double r, double theta)¶ This function returns the complex number
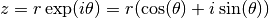 from the polar representation
(
from the polar representation
(r,theta).
Properties of complex numbers¶
-
double
cml_complex_arg(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the argument of the complex number
z,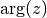 , where
, where 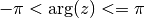 .
.
-
double
cml_complex_abs(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the magnitude of the complex number
z,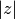 .
.
-
double
cml_complex_abs2(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the squared magnitude of the complex number
z,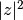 .
.
-
double
cml_complex_logabs(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the natural logarithm of the magnitude of the complex number
z,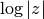 . It allows an accurate
evaluation of
. It allows an accurate
evaluation of 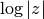 when
when 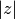 is close to one. The direct
evaluation of
is close to one. The direct
evaluation of log(cml_complex_abs(z))would lead to a loss of precision in this case.
Complex arithmetic operators¶
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_add(cml_complex_t a, cml_complex_t b)¶ This function returns the sum of the complex numbers
aandb,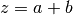 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_sub(cml_complex_t a, cml_complex_t b)¶ This function returns the difference of the complex numbers
aandb,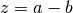 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_mul(cml_complex_t a, cml_complex_t b)¶ This function returns the product of the complex numbers
aandb,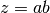 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_div(cml_complex_t a, cml_complex_t b)¶ This function returns the quotient of the complex numbers
aandb,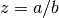 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_add_real(cml_complex_t a, double x)¶ This function returns the sum of the complex number
aand the real numberx,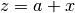 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_sub_real(cml_complex_t a, double x)¶ This function returns the difference of the complex number
aand the real numberx,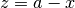 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_mul_real(cml_complex_t a, double x)¶ This function returns the product of the complex number
aand the real numberx,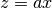 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_div_real(cml_complex_t a, double x)¶ This function returns the quotient of the complex number
aand the real numberx,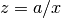 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_add_imag(cml_complex_t a, double y)¶ This function returns the sum of the complex number
aand the imaginary number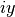 ,
, 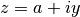 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_sub_imag(cml_complex_t a, double y)¶ This function returns the difference of the complex number
aand the imaginary number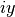 ,
, 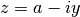 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_mul_imag(cml_complex_t a, double y)¶ This function returns the product of the complex number
aand the imaginary number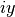 ,
, 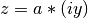 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_div_imag(cml_complex_t a, double y)¶ This function returns the quotient of the complex number
aand the imaginary number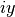 ,
, 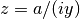 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_conj(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex conjugate of the complex number
z,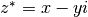 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_inverse(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the inverse, or reciprocal, of the complex number
z,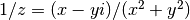 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_negative(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the negative of the complex number
z,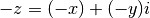 .
.
Elementary Complex Functions¶
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_sqrt(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the square root of the complex number
z,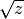 . The branch cut is the negative real axis. The result
always lies in the right half of the complex plane.
. The branch cut is the negative real axis. The result
always lies in the right half of the complex plane.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_sqrt_real(double x)¶ This function returns the complex square root of the real number
x, wherexmay be negative.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_pow(cml_complex_t z, cml_complex_t a)¶ The function returns the complex number
zraised to the complex powera,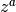 . This is computed as
. This is computed as 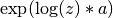 using complex logarithms and complex exponentials.
using complex logarithms and complex exponentials.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_pow_real(cml_complex_t z, double x)¶ This function returns the complex number
zraised to the real powerx,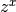 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_exp(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex exponential of the complex number
z,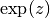 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_log(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex natural logarithm (base
 ) of
the complex number
) of
the complex number z,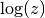 . The branch cut is the
negative real axis.
. The branch cut is the
negative real axis.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_log10(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex base-10 logarithm of the complex number
z,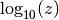 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_log_b(cml_complex_t z, cml_complex_t b)¶ This function returns the complex base-
blogarithm of the complex numberz,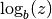 . This quantity is computed as the ratio
. This quantity is computed as the ratio
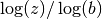 .
.
Complex Trigonometric Functions¶
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_sin(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex sine of the complex number
z,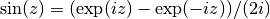 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_cos(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex cosine of the complex number
z,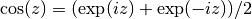 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_tan(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex tangent of the complex number
z,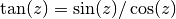 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_sec(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex secant of the complex number
z,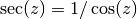 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_csc(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex cosecant of the complex number
z,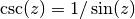 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_cot(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex cotangent of the complex number
z,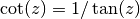 .
.
Inverse Complex Trigonometric Functions¶
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_asin(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex arcsine of the complex number
z,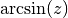 . The branch cuts are on the real axis, less than
. The branch cuts are on the real axis, less than 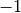 and greater than
and greater than 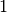 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_asin_real(double z)¶ This function returns the complex arcsine of the real number
z,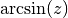 . For
. For  between
between 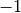 and
and 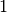 , the
function returns a real value in the range
, the
function returns a real value in the range ![[-\pi/2,\pi/2]](_images/math/66cc619e3f53bbfb9e46f2126bab6db1cda6a056.png) . For
. For
 less than
less than 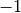 the result has a real part of
the result has a real part of 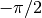 and a positive imaginary part. For
and a positive imaginary part. For  greater than
greater than 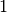 the
result has a real part of
the
result has a real part of 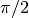 and a negative imaginary part.
and a negative imaginary part.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_acos(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex arccosine of the complex number
z,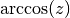 . The branch cuts are on the real axis, less than
. The branch cuts are on the real axis, less than 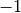 and greater than
and greater than 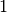 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_acos_real(double z)¶ This function returns the complex arccosine of the real number
z,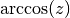 . For
. For  between
between 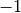 and
and 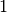 , the
function returns a real value in the range
, the
function returns a real value in the range ![[0,\pi]](_images/math/65fbac805f66f8d00f94040e4e3b2f84d28705a5.png) . For
. For  less than
less than 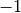 the result has a real part of
the result has a real part of 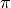 and a
negative imaginary part. For
and a
negative imaginary part. For  greater than
greater than 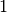 the result
is purely imaginary and positive.
the result
is purely imaginary and positive.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_atan(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex arctangent of the complex number
z, . The branch cuts are on the imaginary axis,
below
. The branch cuts are on the imaginary axis,
below 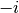 and above
and above 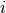 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_asec(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex arcsecant of the complex number
z,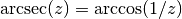 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_asec_real(double z)¶ This function returns the complex arcsecant of the real number
z,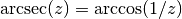 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_acsc(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex arccosecant of the complex number
z,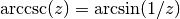 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_acsc_real(double z)¶ This function returns the complex arccosecant of the real number
z,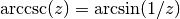 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_acot(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex arccotangent of the complex number
z,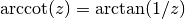 .
.
Complex Hyperbolic Functions¶
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_sinh(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic sine of the complex number
z,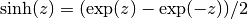 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_cosh(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic cosine of the complex number
z,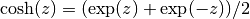 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_tanh(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic tangent of the complex number
z,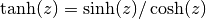 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_sech(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic secant of the complex number
z,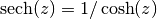 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_csch(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic cosecant of the complex number
z,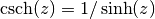 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_coth(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic cotangent of the complex number
z,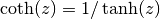 .
.
Inverse Complex Hyperbolic Functions¶
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_asinh(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic arcsine of the complex number
z,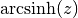 . The branch cuts are on the
imaginary axis, below
. The branch cuts are on the
imaginary axis, below 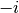 and above
and above 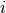 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_acosh(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic arccosine of the complex number
z,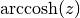 . The branch cut is on the real
axis, less than
. The branch cut is on the real
axis, less than 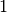 . Note that in this case we use the negative
square root in formula 4.6.21 of Abramowitz & Stegun giving
. Note that in this case we use the negative
square root in formula 4.6.21 of Abramowitz & Stegun giving
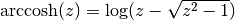 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_acosh_real(double z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic arccosine of the real number
z,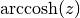 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_atanh(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic arctangent of the complex number
z,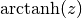 . The branch cuts are on the real
axis, less than
. The branch cuts are on the real
axis, less than 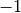 and greater than
and greater than 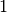 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_atanh_real(double z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic arctangent of the real number
z,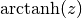 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_asech(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic arcsecant of the complex number
z,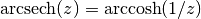 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_acsch(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic arccosecant of the complex number
z,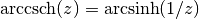 .
.
-
cml_complex_t
cml_complex_acoth(cml_complex_t z)¶ This function returns the complex hyperbolic arccotangent of the complex number
z,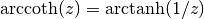 .
.
References and Further Reading¶
The implementations of the elementary and trigonometric functions are based on the following papers,
- T. E. Hull, Thomas F. Fairgrieve, Ping Tak Peter Tang, “Implementing Complex Elementary Functions Using Exception Handling”, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, Volume 20 (1994), pp 215–244, Corrigenda, p553
- T. E. Hull, Thomas F. Fairgrieve, Ping Tak Peter Tang, “Implementing the complex arcsin and arccosine functions using exception handling”, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, Volume 23 (1997) pp 299–335
The general formulas and details of branch cuts can be found in the following books,
- Abramowitz and Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions, “Circular Functions in Terms of Real and Imaginary Parts”, Formulas 4.3.55–58, “Inverse Circular Functions in Terms of Real and Imaginary Parts”, Formulas 4.4.37–39, “Hyperbolic Functions in Terms of Real and Imaginary Parts”, Formulas 4.5.49–52, “Inverse Hyperbolic Functions—relation to Inverse Circular Functions”, Formulas 4.6.14–19.
- Dave Gillespie, Calc Manual, Free Software Foundation, ISBN 1-882114-18-3