Physical Constants¶
This module is inspired by the constants module present in GSL.
The full list of constants is described briefly below. Consult the header files themselves for the values of the constants used in the library.
Fundamental Constants¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_SPEED_OF_LIGHT¶ The speed of light in vacuum,
 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_VACUUM_PERMEABILITY¶ The permeability of free space,
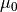 . This constant is defined
in the MKSA system only.
. This constant is defined
in the MKSA system only.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_VACUUM_PERMITTIVITY¶ The permittivity of free space,
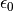 . This constant is
defined in the MKSA system only.
. This constant is
defined in the MKSA system only.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_PLANCKS_CONSTANT_H¶ Planck’s constant,
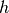 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_PLANCKS_CONSTANT_HBAR¶ Planck’s constant divided by
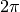 ,
, 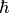 .
.
-
CML_CONST_NUM_AVOGADRO¶ Avogadro’s number,
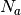 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_FARADAY¶ The molar charge of 1 Faraday.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_BOLTZMANN¶ The Boltzmann constant,
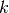 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_MOLAR_GAS¶ The molar gas constant,
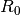 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_STANDARD_GAS_VOLUME¶ The standard gas volume,
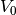 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_STEFAN_BOLTZMANN_CONSTANT¶ The Stefan-Boltzmann radiation constant,
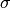 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_GAUSS¶ The magnetic field of 1 Gauss.
Astronomy and Astrophysics¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_ASTRONOMICAL_UNIT¶ The length of 1 astronomical unit (mean earth-sun distance),
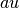 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_GRAVITATIONAL_CONSTANT¶ The gravitational constant,
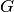 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_LIGHT_YEAR¶ The distance of 1 light-year,
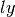 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_PARSEC¶ The distance of 1 parsec,
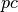 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_GRAV_ACCEL¶ The standard gravitational acceleration on Earth,
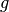 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_SOLAR_MASS¶ The mass of the Sun.
Atomic and Nuclear Physics¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_ELECTRON_CHARGE¶ The charge of the electron,
 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_ELECTRON_VOLT¶ The energy of 1 electron volt,
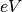 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_UNIFIED_ATOMIC_MASS¶ The unified atomic mass,
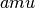 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_MASS_ELECTRON¶ The mass of the electron,
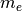 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_MASS_MUON¶ The mass of the muon,
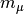 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_MASS_PROTON¶ The mass of the proton,
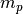 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_MASS_NEUTRON¶ The mass of the neutron,
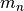 .
.
-
CML_CONST_NUM_FINE_STRUCTURE¶ The electromagnetic fine structure constant
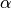 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_RYDBERG¶ The Rydberg constant,
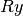 , in units of energy. This is related to
the Rydberg inverse wavelength
, in units of energy. This is related to
the Rydberg inverse wavelength 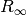 by
by 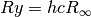 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_BOHR_RADIUS¶ The Bohr radius,
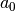 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_ANGSTROM¶ The length of 1 angstrom.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_BARN¶ The area of 1 barn.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_BOHR_MAGNETON¶ The Bohr Magneton,
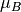 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_NUCLEAR_MAGNETON¶ The Nuclear Magneton,
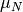 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_ELECTRON_MAGNETIC_MOMENT¶ The absolute value of the magnetic moment of the electron,
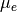 .
The physical magnetic moment of the electron is negative.
.
The physical magnetic moment of the electron is negative.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_PROTON_MAGNETIC_MOMENT¶ The magnetic moment of the proton,
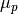 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_THOMSON_CROSS_SECTION¶ The Thomson cross section,
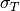 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_DEBYE¶ The electric dipole moment of 1 Debye,
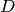 .
.
Measurement of Time¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_MINUTE¶ The number of seconds in 1 minute.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_HOUR¶ The number of seconds in 1 hour.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_DAY¶ The number of seconds in 1 day.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_WEEK¶ The number of seconds in 1 week.
Imperial Units¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_INCH¶ The length of 1 inch.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_FOOT¶ The length of 1 foot.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_YARD¶ The length of 1 yard.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_MILE¶ The length of 1 mile.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_MIL¶ The length of 1 mil (1/1000th of an inch).
Speed and Nautical Units¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_KILOMETERS_PER_HOUR¶ The speed of 1 kilometer per hour.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_MILES_PER_HOUR¶ The speed of 1 mile per hour.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_NAUTICAL_MILE¶ The length of 1 nautical mile.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_FATHOM¶ The length of 1 fathom.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_KNOT¶ The speed of 1 knot.
Printers Units¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_POINT¶ The length of 1 printer’s point (1/72 inch).
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_TEXPOINT¶ The length of 1 TeX point (1/72.27 inch).
Volume, Area and Length¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_MICRON¶ The length of 1 micron.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_HECTARE¶ The area of 1 hectare.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_ACRE¶ The area of 1 acre.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_LITER¶ The volume of 1 liter.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_US_GALLON¶ The volume of 1 US gallon.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_CANADIAN_GALLON¶ The volume of 1 Canadian gallon.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_UK_GALLON¶ The volume of 1 UK gallon.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_QUART¶ The volume of 1 quart.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_PINT¶ The volume of 1 pint.
Mass and Weight¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_POUND_MASS¶ The mass of 1 pound.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_OUNCE_MASS¶ The mass of 1 ounce.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_TON¶ The mass of 1 ton.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_METRIC_TON¶ The mass of 1 metric ton (1000 kg).
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_UK_TON¶ The mass of 1 UK ton.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_TROY_OUNCE¶ The mass of 1 troy ounce.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_CARAT¶ The mass of 1 carat.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_GRAM_FORCE¶ The force of 1 gram weight.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_POUND_FORCE¶ The force of 1 pound weight.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_KILOPOUND_FORCE¶ The force of 1 kilopound weight.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_POUNDAL¶ The force of 1 poundal.
Thermal Energy and Power¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_CALORIE¶ The energy of 1 calorie.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_BTU¶ The energy of 1 British Thermal Unit,
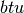 .
.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_THERM¶ The energy of 1 Therm.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_HORSEPOWER¶ The power of 1 horsepower.
Pressure¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_BAR¶ The pressure of 1 bar.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_STD_ATMOSPHERE¶ The pressure of 1 standard atmosphere.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_TORR¶ The pressure of 1 torr.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_METER_OF_MERCURY¶ The pressure of 1 meter of mercury.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_INCH_OF_MERCURY¶ The pressure of 1 inch of mercury.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_INCH_OF_WATER¶ The pressure of 1 inch of water.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_PSI¶ The pressure of 1 pound per square inch.
Viscosity¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_POISE¶ The dynamic viscosity of 1 poise.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_STOKES¶ The kinematic viscosity of 1 stokes.
Light and Illumination¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_STILB¶ The luminance of 1 stilb.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_LUMEN¶ The luminous flux of 1 lumen.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_LUX¶ The illuminance of 1 lux.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_PHOT¶ The illuminance of 1 phot.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_FOOTCANDLE¶ The illuminance of 1 footcandle.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_LAMBERT¶ The luminance of 1 lambert.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_FOOTLAMBERT¶ The luminance of 1 footlambert.
Radioactivity¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_CURIE¶ The activity of 1 curie.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_ROENTGEN¶ The exposure of 1 roentgen.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_RAD¶ The absorbed dose of 1 rad.
Force and Energy¶
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_NEWTON¶ The SI unit of force, 1 Newton.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_DYNE¶ The force of 1 Dyne =
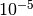 Newton.
Newton.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_JOULE¶ The SI unit of energy, 1 Joule.
-
CML_CONST_MKSA_ERG¶ The energy 1 erg =
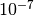 Joule.
Joule.
Prefixes¶
These constants are dimensionless scaling factors.
-
CML_CONST_NUM_YOTTA¶ 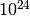
-
CML_CONST_NUM_ZETTA¶ 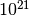
-
CML_CONST_NUM_EXA¶ 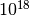
-
CML_CONST_NUM_PETA¶ 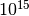
-
CML_CONST_NUM_TERA¶ 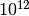
-
CML_CONST_NUM_GIGA¶ 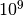
-
CML_CONST_NUM_MEGA¶ 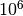
-
CML_CONST_NUM_KILO¶ 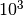
-
CML_CONST_NUM_MILLI¶ 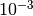
-
CML_CONST_NUM_MICRO¶ 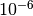
-
CML_CONST_NUM_CML_NANO¶ 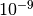
-
CML_CONST_NUM_PICO¶ 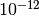
-
CML_CONST_NUM_FEMTO¶ 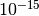
-
CML_CONST_NUM_ATTO¶ 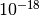
-
CML_CONST_NUM_ZEPTO¶ 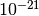
-
CML_CONST_NUM_YOCTO¶ 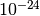
Examples¶
The following program demonstrates the use of the physical constants in a calculation. In this case, the goal is to calculate the range of light-travel times from Earth to Mars.
The required data is the average distance of each planet from the Sun in astronomical units (the eccentricities and inclinations of the orbits will be neglected for the purposes of this calculation). The average radius of the orbit of Mars is 1.52 astronomical units, and for the orbit of Earth it is 1 astronomical unit (by definition). These values are combined with the MKSA values of the constants for the speed of light and the length of an astronomical unit to produce a result for the shortest and longest light-travel times in seconds. The figures are converted into minutes before being displayed.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cml.h>
int
main(void)
{
double c = CML_CONST_MKSA_SPEED_OF_LIGHT;
double au = CML_CONST_MKSA_ASTRONOMICAL_UNIT;
double minutes = CML_CONST_MKSA_MINUTE;
/* distance stored in meters */
double r_earth = 1.00 * au;
double r_mars = 1.52 * au;
double t_min, t_max;
t_min = (r_mars - r_earth) / c;
t_max = (r_mars + r_earth) / c;
printf("light travel time from Earth to Mars:\n");
printf("minimum = %.1f minutes\n", t_min / minutes);
printf("maximum = %.1f minutes\n", t_max / minutes);
return 0;
}
Here is the output from the program,
light travel time from Earth to Mars:
minimum = 4.3 minutes
maximum = 21.0 minutes
References and Further Reading¶
The authoritative sources for physical constants are the 2006 CODATA recommended values, published in the article below. Further information on the values of physical constants is also available from the NIST website.
- P.J. Mohr, B.N. Taylor, D.B. Newell, “CODATA Recommended Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants: 2006”, Reviews of Modern Physics, 80(2), pp. 633–730 (2008).